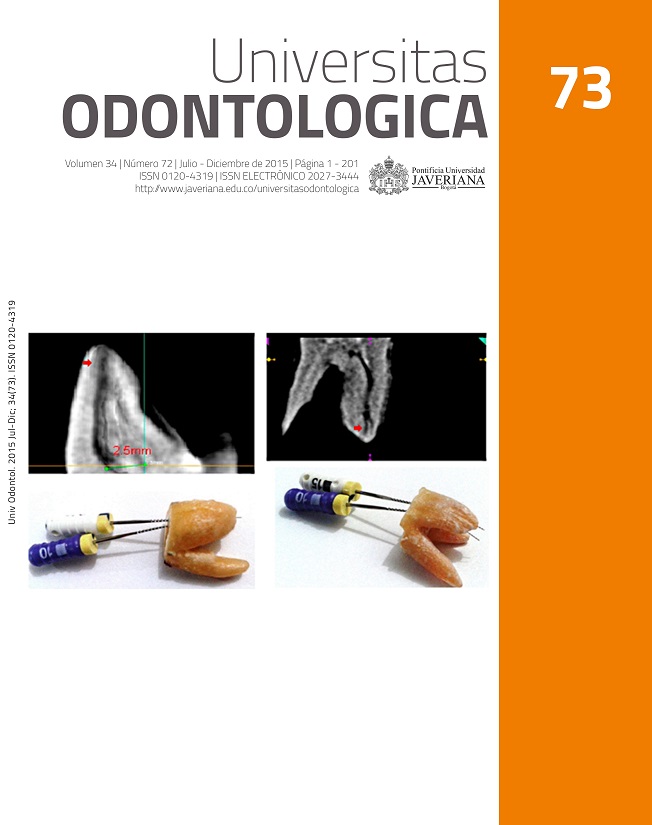
Resumo
RESUMEN. Objetivo: Analizar, mediante la técnica de difractometría de rayos X, las alteraciones en la estructura de las limas primarias con aleación alambre M del sistema WaveOne® (Dentsply Maillefer) después de la preparación del conducto mv1 de un primer molar superior y su posterior esterilización. Métodos: Se evaluaron 2 limas nuevas (grupo 1) y 6 limas usadas y esterilizadas (grupo 2) que fueron empleadas para preparar el conducto mv1 de molares superiores en pacientes que presentaban curvatura moderada. Resultados: Durante la preparación del conducto radicular no se presentó fractura de ningún instrumento. Los patrones de difracción de rayos X del grupo 1 mostraron tres picos principales con similar intensidad, el mismo ancho y posición 2θ. El comportamiento de la mayoría de las limas pertenecientes al grupo 2 exhibió un incremento de sus intensidades posterior a su uso. Se preservó la posición y ancho del pico en las diferentes muestras. Conclusiones: La lima primaria del sistema WaveOne® con aleación alambre M mostró un aumento en la intensidad de sus fases sin variación en la cantidad de picos, situación que sugiere que no se presenta daño en la aleación.
ABSTRACT. Objective: To analyze structural changes of WaveOne® (Dentsply Maillefer) primary files (M-Wire alloy) after preparation of an upper first molar mv1 canal and subsequent sterilization. Methods: The analysis included 2 new (group 1) and 6 used and sterilized files (group 2) that were used to prepare the mesial buccal root canal of maxillary molars with moderate curvature. Structure was evaluated through X-ray diffractometry. Results: None of the instruments broke during canal preparation. X-ray diffraction patterns for group 1 showed 3 main peaks with similar intensity, same width, and 2θ position. Most group 2 files showed intensity increases after used. Peak and width stayed stable afterwards in most samples. Conclusion: WaveOne® primary file with M-Wire alloy exhibited an intensity increase in every phases and same number of peaks, which suggests there was not any damage to the alloy.
Civjan S, Huget EF, Sesimon LB. Potential applications of certain nickel-titanium (Nitinol) Alloys. J Dent Res. 1975; 54(1): 89-96.
Shen Y, Zhou HM, Wang Z, Campbell L, Zheng YF, Haapasalo M. Phase transformation behavior and mechanical properties of thermomechanically treated K3XF nickel-titanium instruments. J Endod. 2013; 39(7): 919-23.
Thompson S. An overview of nickel–titanium alloys used in dentistry. Int Endod J. 2000; 33(4): 297-310.
Sattapan B, Nervo G, Palamara J, Messer H. Defects in rotary nickel-titanium files after clinical use. J Endod. 2000; 26(3): 161-5.
Zhou HM, Shen Y, Zheng W, Li L, Zheng YF, Haapasalo M. Mechanical properties of controlled memory and superelastic nickel-titanium wires used in the manufacture of rotary endodontic instruments. J Endod. 2012; 38(11): 1535-40.
Ye J, Gao Y. Metallurgical characterization of M-Wire nickel-titanium shape memory alloy used for endodontic rotary instruments during low-cycle fatigue. J Endod. 2012; 38(1): 105-7.
Pereira ES, Gomes RO, Leroy AM, Singh R, Peters OA, Bahia MG, Buono VT. Mechanical behavior of M-Wire and conventional NiTi wire used to manufacture rotary endodontic instruments. Dent Mater. 2013; 29(12): 318-24.
Shen Y, Qian W, Abtin H, Gao Y, Haapasalo M. Effect of environment on fatigue failure of controlled memory wire nickel-titanium rotary instruments. J Endod. 2012; 38(3): 376-80.
Gutmann J, Gao Y. Alteration in the inherent metallic and surface properties of nickel-titanium root canal instruments to enhance performance, durability and safety: a focused review. Int Endod J. 2012; 45(2): 113-28.
Plotino G, Grande NM, Cotti E, Testarelli L, Gambarini G. Blue Treatment enhances cyclic fatigue resistance of Vortex nickel-titanium rotary files. J Endod. 2014; 40(9): 1451-3.
Hayashi Y, Yoneyama T, Yahata Y, Miyai K, Doi H, Hanawa T, Ebihara A, Suda H. Phase transformation behaviour and bending properties of hybrid nickel–titanium rotary endodontic instruments. Int Endod J. 2007; 40: 247-53.
Alapati SB, Brantley WA, Iijima M, Clark WA, Kovarik L, Buie C, Liu J, Ben Johnson W. Metallurgical characterization of a new nickel-titanium wire for rotary endodontic instruments. J Endod. 2009; (35)11: 1589-93.
Pirani C, Paolucci A, Ruggeri O, Bossù M, Polimeni A, Gatto MR, Gandolfi MG, Prati C. Wear and metallographic analysis of WaveOne and Reciproc NiTi instruments before and after three uses in root canals. Scanning. 201; 36(5): 517-25.
Giuliani V, Di Nasso L, Pace R, Pagavino G. Shaping ability of WaveOne® primary reciprocating files and Pro Taper system used in continuous and reciprocating motion. J Endod. 2014; 40(9): 1468-71.
Gao Y, Gutmann JL, Wilkinson K, Maxwell R, Ammon D. Evaluation of the impact of raw materials on the fatigue and mechanical properties of profile Vortex rotary instruments. J Endod. 2012; 38(3): 398-401.
Miyazaki S, Otzuka K. Development of shape memory alloys. ISIJ Internat. 1989; 29(5): 353-77.
Tobushi H, Hachisuka T, Yamada S, Lin PH. Rotating-bending fatigue of a NiTi shape-memory alloy wire. Mech Mater. 1997; 26: 35-42.
Lopes HP, Gambarra-Soares T, Elias CN, Siqueira JF Jr, Inojosa IF, Lopes WS, Vieira VT. Comparison of the mechanical properties of rotary instruments made of conventional nickel-titanium wire, M-wire, or nickel-titanium alloy in R-phase. J Endod. 2013; 39(4): 516-20.
Shen Y, Coil JM, Zhou H, Zheng Y, Haapasalo M. HyFlex nickel-titanium rotary instruments after clinical use: metallurgical properties. Int Endod J. 2013; 46(8): 720-9.
Krishnan M, Seema S, Sukumaran K, Pawar V. Phase transitions in coated nickel titanium arch wires: A differential scanning calorimetric and X-ray diffraction analysis. Bull Mater Sci. 2012; 35(5): 905-11.
Webber J, Machtou P, Pertot W, Kuttler S, Ruddle C, West J. The WaveOne single-file reciprocating system. Roots. 2011; 1: 28-33.
Cunha RS, Junaid A, Ensinas P, Nudera W, Bueno CE. Assessment of the separation incidence of reciprocating WaveOne files: a prospective clinical study. J Endod. 2014; 40(7): 922-4.
Pertot WJ. Sistema Waveone (Dentsply Maillefer). Conformación radicular usando una lima única con movimientos de rotación alterna. Blog Cátedra de Endodoncia, Asociación Odontológica Argentina. 17 Marzo 2011. Disponible en línea en: http://endodonciaargentina.blogspot.com.co/2011/03/sistema-waveone-dentsply-maillefer.html.
Arias A, Perez-Higueras J, De la Macorra J. Influence of clinical usage of GT and GTX files on cyclic fatigue resistance. Int Endod J. 2014; 47(3): 257-63.
Shen Y, Coil JM, Zhou HM, Tam E, Zheng YF, Haapasalo M. Profile Vortex instruments after clinical use: a metallurgical properties study. J Endod. 2012; 38(12): 1613-7.
Huamán J. Comparación de la técnica manual con la tecnica rotatoria del sistema k3 y del sistema profile GT en la preparación biomecánica de conductos curvos. [Trabajo de pregrado en odontología]. Lima, Perú: Universidad Nacional Mayor de San Marcos; 2003.
Forero LE, Vesga W. Transformaciones de fase y comportamiento mecánico bajo cargas cíclicas de una aleación binaria Ni-Ti. Scientia et Technica. 2007; XIII(36): 821-6.
Braz F, Oliveira J, Machado A, Schell N. XRD Study of NiTi endodontic files using synchrotron radiation. J Mater Eng Perform. 2014; 23(7): 2477-81.
Shen Y, Peng B, Cheung GS. Factors associated with the removal of fractured NiTi instruments from root canal systems. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral Radiol Endod. 2004; 98(5): 605-10.
Shen Y, Zhou HM, Zheng YF, Campbell L, Peng B, Haapasalo M. Metallurgical characterization of controlled memory wire nickel-titanium rotary instruments. J Endod. 2011; 37(11): 1566-71.
Yahata Y, Yoneyama T, Hayashi Y, Ebihara A, Doi H, Hanawa T, Suda H. Effect of heat treatment on transformation temperatures and bending properties of nickel-titanium endodontic instruments. Int Endod J. 2009; 42(7): 621-6.
Iijima M, Ohno H, Kawashima I, Endo K, Brantley WA, Mizoguchi I. Micro X-ray diffraction study of superelastic nickel–titanium orthodontic wires at different temperatures and stresses. Biomater. 2002; 23(8): 1769-74.
Gluskin A, Brown D, Buchanan L. A reconstructed computerized tomographic comparison of Ni-Ti rotary GT files versus traditional instruments in canals shaped by novice operators. Int Endod J. 2001; 34(6): 476-84.
Fernández Ponce de León YF, Mendiola Aquino C. Evolución de los sistemas rotatorios en endodoncia: propiedades y diseño. Rev Estomatol Herediana. 2011; 21(1): 51-4.
Montalvão D, Alçada FS, Braz Fernandes FM, de Vilaverde-Correia S. Structural characterisation and mechanical FE analysis of conventional and M-Wire Ni-Ti alloys used in endodontic rotary instruments. Scientific World J. 2014; 1: 1-8.
Pirani C, Ruggeri O, Cirulli PP, Pelliccioni GA, Gandolfi MG, Prati C. Metallurgical analysis and fatigue resistance of WaveOne and Protaper nickel-titanium instruments. Odontology 2014; 102(2): 211-6.
Este periódico científico está registrado sob a licença Creative Commons Atribuição 4.0 Internacional. Portanto, este trabalho pode ser reproduzido, distribuído e comunicado publicamente em formato digital, desde que os autores e a Pontifícia Universidade Javeriana sejam reconhecidos. Citar, adaptar, transformar, autoarquivar, republicar e criar novas obras a partir do material é permitido para qualquer finalidade (mesmo comercial), desde que a autoria seja devidamente reconhecida, um link para o trabalho original seja fornecido e quaisquer alterações sejam indicadas. A Pontifícia Universidade Javeriana não detém os direitos sobre os trabalhos publicados, e o conteúdo é de exclusiva responsabilidade dos autores, que mantêm seus direitos morais, intelectuais, de privacidade e de publicidade.