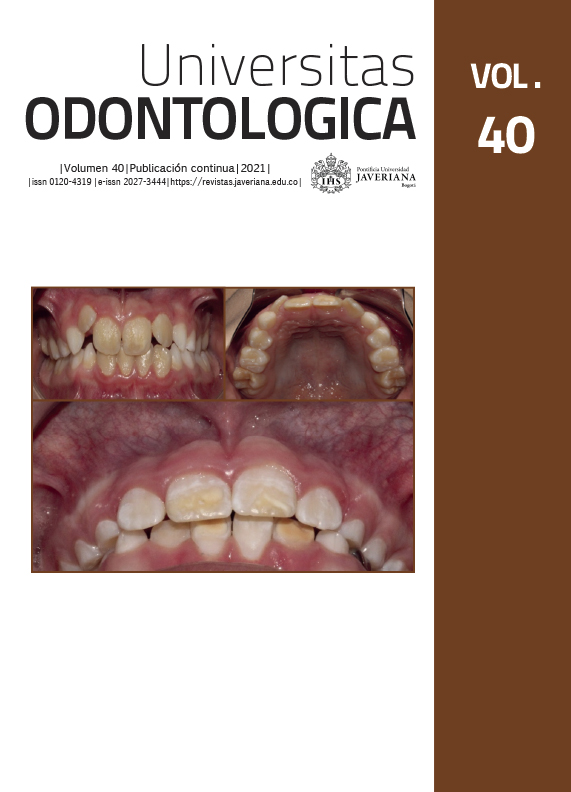
Resumen
Antecedentes: La hipofosfatemia ligada al cromosoma X (HLX) es una enfermedad genética rara en la que el aumento de la pérdida de fosfato en el riñón conduce a la hipofosfatemia y evita la mineralización normal de los huesos y tejidos duros del diente. Objetivo: Analizar el impacto que tiene esta patología genética sobre los tejidos duros dentales y periodontales tales como dentina, cemento y hueso alveolar. Método: Se realizo una revisión integradora de la literatura a partir de búsquedas en las bases de PubMed y SciELO. Los términos de búsqueda fueron hipofosfatemia ligada a X, tejido dental, periodonto, dentina, esmalte, cemento y hueso alveolar. La búsqueda se restringió a literatura en español e inglés publicada entre 2000 y 2020. Resultados: Se incluyeron 13 artículos que daban cuenta del impacto de la hipofosfatemia sobre los tejidos dentales, principalmente sobre la dentina y el cemento. También se informa de un impacto negativo de la hipofosfatemia sobre los tejidos periodontales especialmente sobre el hueso alveolar. Conclusiones: Los hallazgos de la presente revisión integradora muestran que la HLX altera la estructura de los tejidos duros de cavidad oral, lo cual afecta la calidad de vida de los pacientes. Genera la necesidad de seguir investigando sobre el efecto y el comportamiento de esta patología sobre los tejidos duros de cavidad oral, así como su comportamiento como factor de riesgo para la presencia de enfermedad dental y periodontal.
Emma F, Cappa M, Antoniazzi F, Bianchi ML, Chiodini I, Eller Vainicher C, Di Iorgi N, Maghnie M, Cassio A, Balsamo A, Baronio F, de Sanctis L, Tessaris D, Baroncelli GI, Mora S, Brandi ML, Weber G, D'Ausilio A, Lanati EP. X-linked hypophosphatemic rickets: an Italian experts' opinion survey. Ital J Pediatr. 2019 May 31; 45(1): 67. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13052-019-0654-6
Biosse Duplan M, Coyac BR, Bardet C, Zadikian C, Rothenbuhler A, Kamenicky P, Briot K, Linglart A, Chaussain C. Phosphate and Vitamin D Prevent Periodontitis in X-Linked Hypophosphatemia. J Dent Res. 2017 Apr; 96(4): 388-395. https://doi.org/10.1177/0022034516677528
Haffner D, Waldegger S. Trastornos del metabolismo del fósforo. En: Geary DF, Schaefer F, editores. Enfermedad renal pediátrica. Berlín Heidelberg: Springer-Verlag; 2016. p. 953-972
Wang H, Yoshiko Y, Yamamoto R, Minamizaki T, Kozai K, Tanne K, Aubin JE, Maeda N. Overexpression of fibroblast growth factor 23 suppresses osteoblast differentiation and matrix mineralization in vitro. J Bone Miner Res. 2008 Jun; 23(6): 939-948. https://doi.org/10.1359/jbmr.080220
Linglart A, Biosse-Duplan M, Briot K, Chaussain C, Esterle L, Guillaume-Czitrom S, Kamenicky P, Nevoux J, Prié D, Rothenbuhler A, Wicart P, Harvengt P. Therapeutic management of hypophosphatemic rickets from infancy to adulthood. Endocr Connect. 2014 Mar 14; 3(1): 13-30. https://doi.org/10.1530/EC-13-0103
Levy-Litan V, Hershkovitz E, Avizov L, Leventhal N, Bercovich D, Chalifa-Caspi V, Manor E, Buriakovsky S, Hadad Y, Goding J, Parvari R. Autosomal-recessive hypophosphatemic rickets is associated with an inactivation mutation in the ENPP1 gene. Am J Hum Genet. 2010 Feb 12; 86(2): 273-278. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ajhg.2010.01.010
Shimada T, Mizutani S, Muto T, Yoneya T, Hino R, Takeda S, Takeuchi Y, Fujita T, Fukumoto S, Yamashita T. Cloning and characterization of FGF23 as a causative factor of tumor-induced osteomalacia. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2001 May 22; 98(11): 6500-6505. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.101545198
Whittemore R, Knafl K. The integrative review: updated methodology. J Adv Nurs. 2005 Dec; 52(5): 546-553. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365
Rabbani A, Rahmani P, Ziaee V, Ghodoosi S. Dental problems in hypophosphatemic rickets, a cross sectional study. Iran J Pediatr. 2012 Dec; 22(4): 531-534.
Salmon B, Bardet C, Coyac BR, Baroukh B, Naji J, Rowe PS, Opsahl Vital S, Linglart A, Mckee MD, Chaussain C. Abnormal osteopontin and matrix extracellular phosphoglycoprotein localization, and odontoblast differentiation, in X-linked hypophosphatemic teeth. Connect Tissue Res. 2014 Aug;55 Suppl 1:79-82. https://doi.org/10.3109/03008207.2014.923864
Fisher LW, Fedarko NS. Six genes expressed in bones and teeth encode the current members of the SIBLING family of proteins. Connect Tissue Res. 2003; 44 Suppl 1: 33-40
Baroncelli GI, Angiolini M, Ninni E, Galli V, Saggese R, Giuca MR. Prevalence and pathogenesis of dental and periodontal lesions in children with X-linked hypophosphatemic rickets. Eur J Paediatr Dent. 2006 Jun; 7(2): 61-66.
Souza AP, Kobayashi TY, Lourenço Neto N, Silva SM, Machado MA, Oliveira TM. Dental manifestations of patient with vitamin D-resistant rickets. J Appl Oral Sci. 2013 Nov-Dec;21(6):601-6. https://doi.org/10.1590/1679-775720130249
Boukpessi T, Hoac B, Coyac BR, Leger T, Garcia C, Wicart P, Whyte MP, Glorieux FH, Linglart A, Chaussain C, McKee MD. Osteopontin and the dento-osseous pathobiology of X-linked hypophosphatemia. Bone. 2017 Feb; 95: 151-161. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bone.2016.11.019
Coyac BR, Hoac B, Chafey P, Falgayrac G, Slimani L, Rowe PS, Penel G, Linglart A, McKee MD, Chaussain C, Bardet C. Defective Mineralization in X-Linked Hypophosphatemia Dental Pulp Cell Cultures. J Dent Res. 2018 Feb;97(2):184-191. https://doi.org/10.1177/0022034517728497
Coyac BR, Falgayrac G, Penel G, Schmitt A, Schinke T, Linglart A, McKee MD, Chaussain C, Bardet C. Impaired mineral quality in dentin in X-linked hypophosphatemia. Connect Tissue Res. 2018 Dec; 59(sup1): 91-96. https://doi.org/10.1080/03008207.2017.1417989
Ye L, Liu R, White N, Alon US, Cobb CM. Periodontal status of patients with hypophosphatemic rickets: a case series. J Periodontol. 2011 Nov; 82(11): 1530-1535. https://doi.org/10.1902/jop.2011.100736
Ye L, Zhang S, Ke H, Bonewald LF, Feng JQ. Periodontal breakdown in the Dmp1 null mouse model of hypophosphatemic rickets. J Dent Res. 2008 Jul; 87(7): 624-629. https://doi.org/10.1177/154405910808700708
Zhang H, Chavez MB, Kolli TN, Tan MH, Fong H, Chu EY, Li Y, Ren X, Watanabe K, Kim DG, Foster BL. Dentoalveolar Defects in the Hyp Mouse Model of X-linked Hypophosphatemia. J Dent Res. 2020 Apr; 99(4): 419-428. https://doi.org/10.1177/0022034520901719
Connor J, Olear EA, Insogna KL, Katz L, Baker S, Kaur R, Simpson CA, Sterpka J, Dubrow R, Zhang JH, Carpenter TO. Conventional Therapy in Adults With X-Linked Hypophosphatemia: Effects on Enthesopathy and Dental Disease. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2015 Oct; 100(10): 3625-3632. https://doi.org/10.1210/JC.2015-2199

Esta obra está bajo una licencia internacional Creative Commons Atribución 4.0.
Derechos de autor 2021 Francina Maria Escobar Arregocés