Abstract
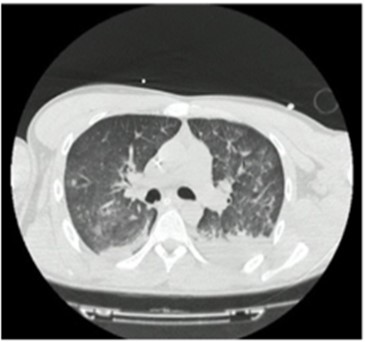
Bronchiolitis obliterans (BO) is characterized by being a chronic obstructive respiratory disease with irreversible histological changes and an unusual presentation in the pediatric population, for which reason it is underdiagnosed, however, in broncho-obstructive episodes of atypical or severe evolution, it should be considered as a diagnosis. Obliterative bronchiolitis is considered a chronic inflammatory disease of the bronchioles that can present in two histopathological ways, either by peribronchiolar involvement from the epithelium towards the lumen in a concentric (constrictive) way or by the occupation of the bronchiole lumen due to proliferation of endoluminal tissue (proliferative). The diagnosis is made according to clinical criteria and radiological criteria (chest CT), a score greater than 7 predicts with high precision the diagnosis of obliterative bronchiolitis. Since it is a chronic inflammatory disease mediated by the immune response, treatment is aimed at suppressing the inflammatory response to avoid lung damage due to irreversible changes, however, once the disease is established, treatment will be symptomatic, supportive, and follow-up of lung function. Next, the case of a 2-month-old infant with a history of respiratory infection due to SARS-CoV-2 (COVID-19) in his neonatal period is presented, in whom radiological and clinical changes compatible with post-infectious constrictive bronchiolitis were evidenced in its clinical evolution.
Kurland, G. and Michelson, P. (2005), Bronchiolitis obliterans in children. Pediatr. Pulmonol., 39: 193-208. https://doi.org/10.1002/ppul.20145
Jerkic SP, Brinkmann F, Calder A, Casey A, Dishop M, Griese M, et al. Postinfectious Bronchiolitis Obliterans in Children: Diagnostic Workup and Therapeutic Options: A Workshop Report. Can Respir J. 2020;2020.
Yu J. Postinfectious bronchiolitis obliterans in children: lessons from bronchiolitis obliterans after lung transplantation and hematopoietic stem cell transplantation. Korean J Pediatr. 2015;58(12):459–65.
Barker AF, Bergeron A, Rom WN, Hertz MI. Obliterative bronchiolitis. N Engl J Med. 2014;370(19):1820–8.
Colom AJ, Teper AM, Vollmer WM, et al. Risk factors for the development of bronchiolitis obliterans in children with bronchiolitis. Thorax
;107(2):160-7
Kavaliunaite E, Aurora P. Diagnosing and managing bronchiolitis obliterans in children. Expert Rev Respir Med. 2019;13(5):481–8.
Lamot S, López AM, Bergna M, Spina JC, Villa J, Martín V, et al. RAMR - Volumen 14, Número 3 - Obstrucción crónica de la vía aérea en un paciente de 18 años [Internet]. Ramr.org. [citado el 17 de marzo de 2021]. Disponible en: http://www.ramr.org/articulos/volumen_14_numero_3/ateneo/ateneo_obstruccion_cronica_via_aerea_paciente_18_anios.php
Mattiello R, Sarria EE, Stein R, Fischer GB, Mocelin HT, Barreto SS, et al. Functional capacity assessment during exercise in children and adolescents with post-infectious bronchiolitis obliterans. J Pediatr (Rio J). 2008;84(4):337-343.
Fischer GB, Sarria EE, Mattiello R, Mocelin HT, Castro-Rodriguez JA. Post infectious bronchiolitis obliterans in children. Paediatr Respir Rev.
;11(4):233–9.
Obliterans PB. Bronquiolitis obliterante posinfecciosa Comité Nacional de Neumonología. Arch Argent Pediatr [Internet]. 2018;116(03). Disponible en: https://www.sap.org.ar/docs/publicaciones/archivosarg/2018/v116n3a31s.pdf
Mansbach JM, Hasegawa K, Piedra PA, Sullivan AF, Camargo CA Jr. Severe Coronavirus bronchiolitis in the pre-COVID-19 era. Pediatrics. 2020;146(3):e20201267.
Yilmaz O, Gochicoa‐Rangel L, Blau H, et al. Brief report: international perspectives on the pediatric COVID‐19 experience. Pediatr Pulmonol. 2020; 55(7): 1598‐ 1600
Rodríguez MS. La bronquiolitis en el año del COVID-19. Arch Argent Pediatr 2020;118(3):222-223.
Grimaud E, Challiol M, Guilbaud C, Delestrain C, Madhi F, Ngo J, et al. Delayed acute bronchiolitis in infants hospitalized for COVID-19. Pediatr Pulmonol. 2020;55(9):2211–2.

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
Copyright (c) 2022 Maria Isabel Garcia Moya, Laura Carolina Rodríguez , Sonia Maria Restrepo Gualteros , Olga Patricia Panqueva Centanaro, Luis Felipe Uriza Carrasco